Basic Distribution Constraints
In SystemVerilog, almost all constraints are some form of boolean expression. The constraint solver’s job is to satisfy all these boolean expression when choosing random values. The two exceptions to this are solve before constraints, which control the order of value resolution, and dist constraints, witch control the distribution of values chosen. This latter type of constraint is what we are looking at in this post.
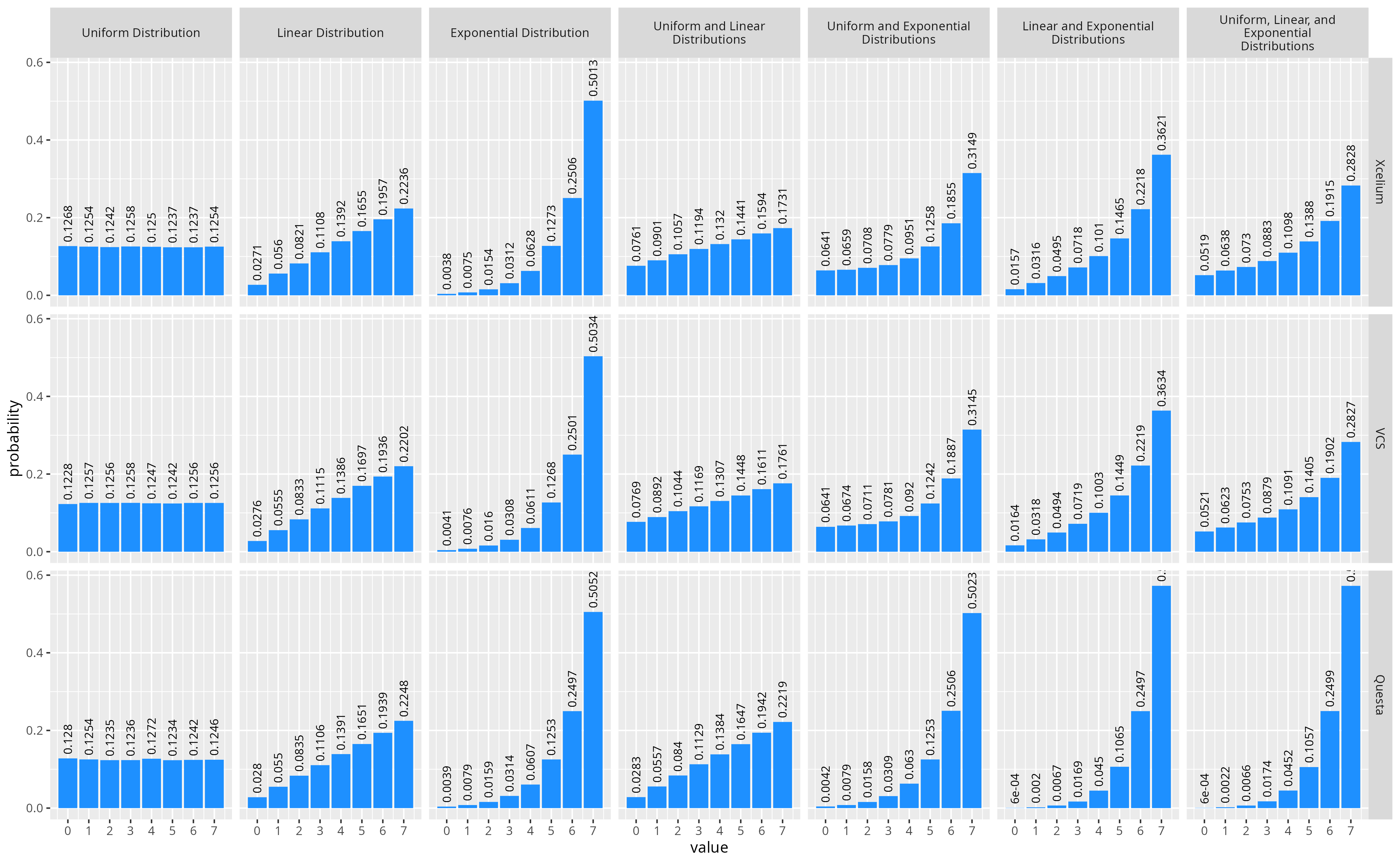
At a high level the distribution constraint provides a syntax for defining the probability mass function for a random variable over a given range of discrete values. Below are two examples of dist constraints and the resulting distribution of values over 100k randomizations. The first specifies linearly increasing probability over four values, while the second shows exponentially increasing probability for the same values.